We’ve switched to git at work a few month ago. Not an easy task but the rewards are worth the trouble. Our branching model was based on Git Flow because it’s well documented and gives you a structure to start with DVCS. Well, after a few iterations it wasn’t working as expected in our context. So we had to come up with our own workflow.
I guess Git Flow works well on a clean code base with good test coverage. But on legacy code, where one feature means two regressions, a release branch is like the vietnam war, you never know when you will get out of it. That was one of our main problem on subversion, we were creating release branch to go to production. And it would take forever to actually ship the code. Meanwhile all other development efforts remain stuck.
I though that cheap branching and merging in git would solve our issue. But cheap merging is not enough, you also need to be able to easily pick what to merge. And with Git Flow it’s not easy to remove a feature from a release branch once it’s there. Because a feature branch is started from develop it is bound by its parents commits to other features not yet in production. As a result, if you merge a feature without rebasing you always get more commits than wanted.
So here is the workflow we use to solve those issues:
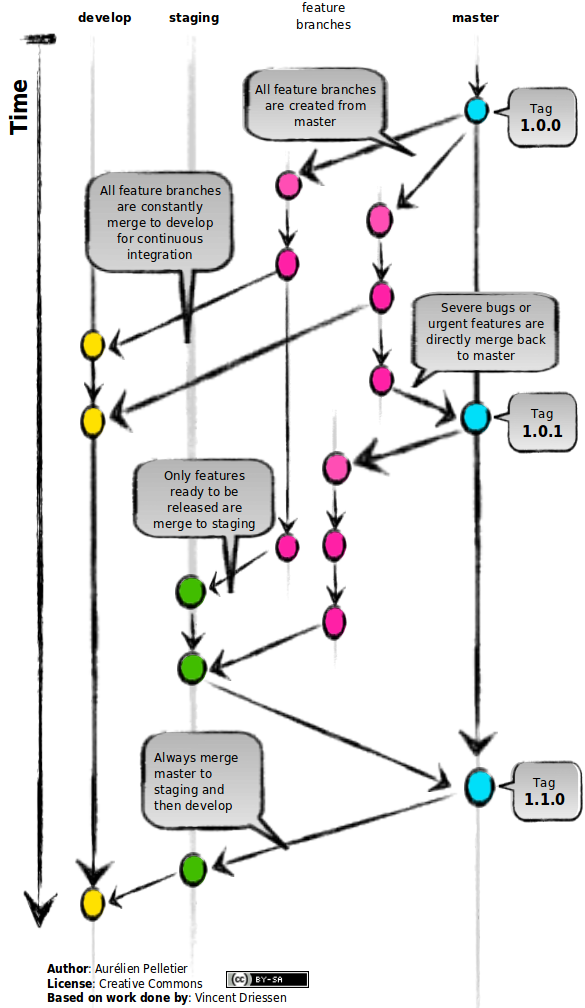
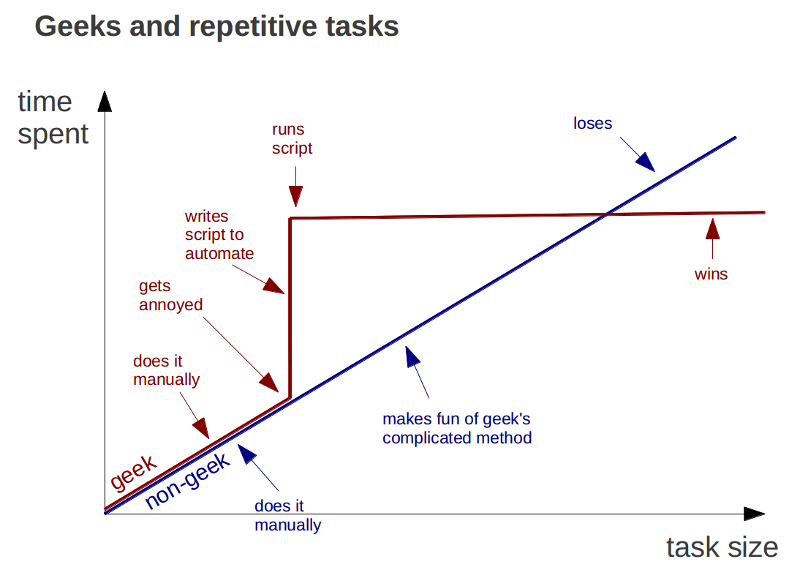
The main branches
We have three branches with an infinite lifetime based on the classical trio (dev/test/prod):
Master is the same as in git flow:
We consider origin/master to be the main branch where the source code of HEAD always reflects aproduction-ready state.
Staging is a bit like develop in Git Flow :
We consider origin/develop to be the main branch where the source code of HEAD always reflects a state with the latest delivered development changes for the next release. Some would call this the “integration branch”.
Develop is there for continuous integration, this is where we constanly merge all the changes to detect bugs and conflicts as soon as possible. The source code in the develop branch never reach a stable point where it is ready to be released. Instead only some feature branches reach a stable point. Those stable feature branches are merge into the staging branch. Since feature branches were created from master and not from develop we can pick individualy which one will be merge to staging. In fact this is the main point of this workflow: We can easily choose which features will go into production next.
To release the code to production we just merge staging into master.
Feature Branches
All work is done in feature branches which can be merge into
- master for a quick fix in production
- staging for bug fixes
- develop constanly for continuous integration
Since we use github we usualy do a pull request to merge feature branches. We don’t always follow the rules and commit on master and staging happens, they are merge back to staging and develop. The only place where we don’t commit is develop 😉 (only merge commit)
Summary
Git Flow was not working for us, but by creating feature branches from master instead of develop we gained the ability to easily choose which features we release next. This gave us much more flexibility and got us out of “vietnam release branch”.
Now I should tell about all the best practices to make this workflow really work, but I’m lucky, someone already wrote them down.
And you, what is your branching model ?